Hematology is a medical field that deals with the study of blood, blood-forming organs like bone marrow. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating various blood related disorders and illnesses. In this blog post, we are going to understand the importance of staining, its different types, techniques, uses and limitations of stains in hematology.
Importance of Staining in Hematology:
Hematology relies on different diagnostic tools, with staining techniques being one of the most crucial. Staining aids in distinguishing between different blood cell types and detecting any abnormal changes that might exist.
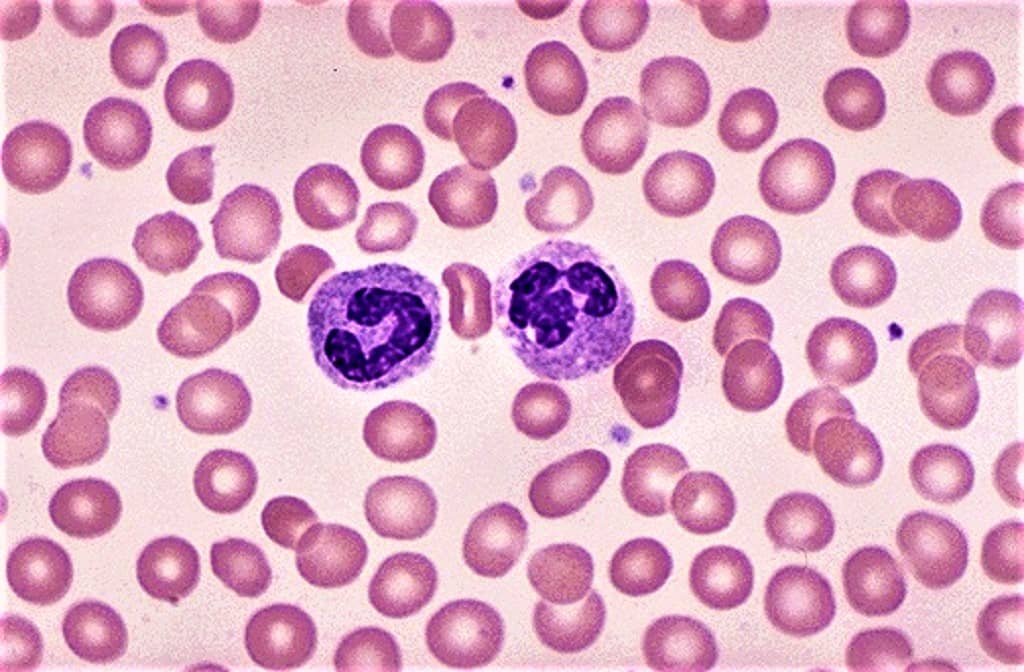
Hematology stains and reagents play a crucial role in clinical and medical cytology research. They make it easier to visualize and identify blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system components through staining. Whether you’re processing samples manually or automatically, the Wright, Giemsa, and Leishman formulations work efficiently on prepared blood smears. These stains are designed to work rapidly, ensuring accurate results even with time-sensitive samples.
Types of Blood Stains:
There are different types of stains that can be used in hematology. The choice of stain depends on the intended objective. Some of the common stains used include Wright stain, Giemsa stain, and Romanowsky stains.
- Giemsa, another widely used stain, may not adequately stain red blood cells, platelets, or white blood cell cytoplasm’s when used alone. It is used to stain parasites such as malaria.
- Romanowsky stain solutions, which consist of methylene blue, oxidative products of methylene blue (Azure A, Azure B, Azure C, and Thionine), and eosin dyes, are commonly used in hematology. Romanowsky stains, on the other hand, provide a more detailed look at the cellular structure and the presence of any anomalies present.
- The Wright stain is classically a mixture of eosin (red) and methylene blue dyes. The Wright stain is used to visualize different cell types in the blood. It is used primarily to stain peripheral blood smears, urine samples, and bone marrow aspirates, which are examined under a light microscope.
Techniques of Staining:
To properly see the cells, blood staining involves a series of steps. First, the blood is fixed and dried onto a slide. Then, the slide is stained and rinsed with a buffer solution. Finally, the slide is observed under a microscope. It’s important for a skilled hematology technician to follow specific guidelines to ensure accurate and consistent results.
Uses of Staining in Diagnosis:
Staining is a fundamental technique in hematology diagnosis that is widely used for various purposes. By applying specific dyes to blood samples, technicians are able to enhance the visibility of cellular components, allowing for a more detailed examination under the microscope.
When the stained slide is examined, the technician can easily identify and differentiate between red and white blood cells. This is crucial in determining the quantity of each cell type present in the sample. Abnormalities in the number of red blood cells may indicate conditions such as anemia, while an abnormal increase or decrease in white blood cells can be indicative of infections or certain types of leukemia. staining is an essential technique in hematology diagnosis that provides valuable information about the quantity, shape, size, and irregularities of blood cells.
By utilizing staining techniques, technicians are able to contribute significantly to the accurate diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Hematology Stains
Reliably differentiate and diagnose blood, and bone marrow samples with your preferred protocol by selecting from our full range of high-quality hematological staining solutions.
List of Chemicals
Type of Hematology Stains
Amyloid
Carbohydrates
Neuronal Tissue
Triglycerides & Lipids
Reticulin Fibers
Connective Muscle Tissue
Pigment, Minerals & Granules
Microorganisms
Limitations of Staining techniques:
Staining plays a vital role in hematology diagnosis as it allows for the visualization and identification of various blood cells and pathogens. However, it is important to acknowledge that staining does have its limitations, which can impact the accuracy and clarity of the results obtained.
Contamination is a significant limitation, as external substances can interfere with the staining process. Differentiating between certain cell types can also be challenging, especially when they have similar staining characteristics. Some infections may not be effectively stained, making it difficult to identify and diagnose them.
To overcome these limitations, proper staining techniques and additional diagnostic tools should be used. Incorporating other methods like molecular testing or flow cytometry can enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Staining techniques may have their limitations, but thanks to the progress of modern technology, we can look forward to even more advanced diagnostic tools in the future. To ensure the best outcomes, hematology technicians need to keep up with the evolving trends in staining techniques and maintain quality assurance.
To achieve the desire results in Hematology for any Hematologist requires authentic Reagents, Solvents, Stains etc. One should choose wisely quality products from reputed brands like “TriStains”, which give you reproducible results. TriStains brand meet the highest quality standards & give excellent color performance of desired components of cells and tissue in life science laboratories. “TriStains”, Biological Stains that offer range of stains used in Histology, Cytology, microbiology & Hematology laboratories. Tristains brand was founded with the vision of providing researchers and medical professionals with the best products available in the market. Buy now the authentic reagents with ISO 9001:2015 quality assurance from www.dawnscientific.com or www.tristains.com.