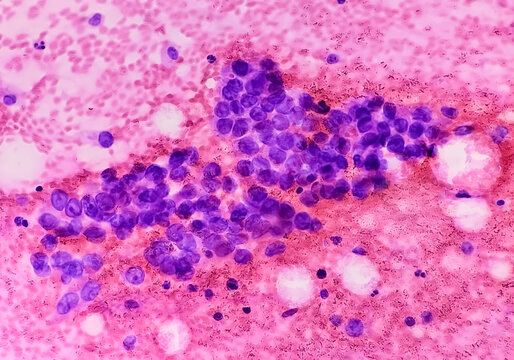
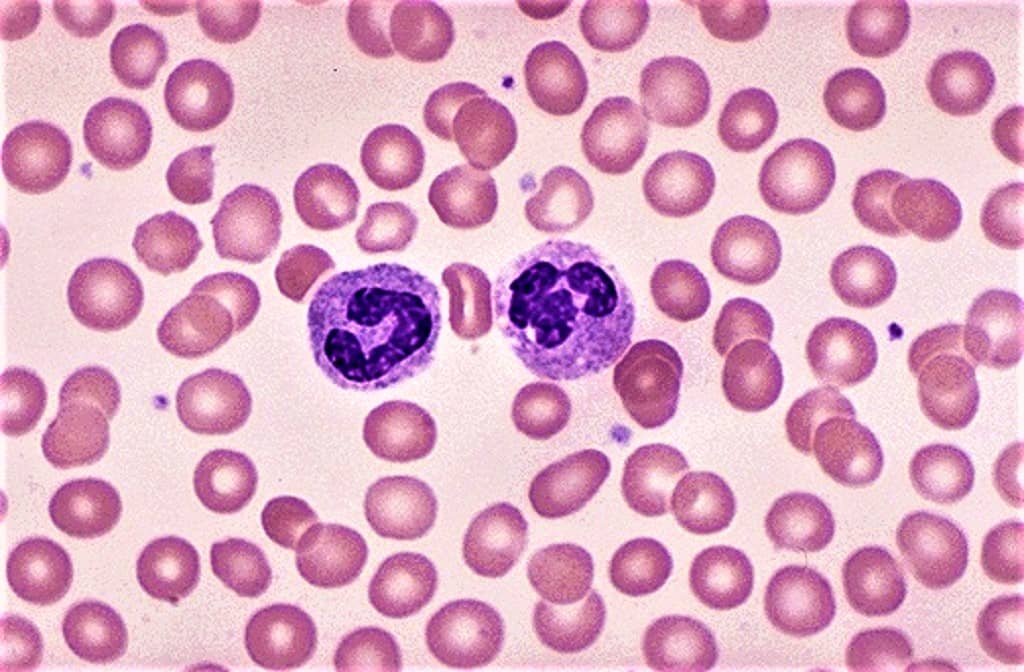
Understanding the Study of Cytology
Cytology or Cytopathology is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. It is also called cytopathology and the study of cells via microscopy. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1928. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments. In this blog post, we are going to understand the study of cytology which includes description of cytology, its branches, its benefits and when its needed for testing.
What is cytology?
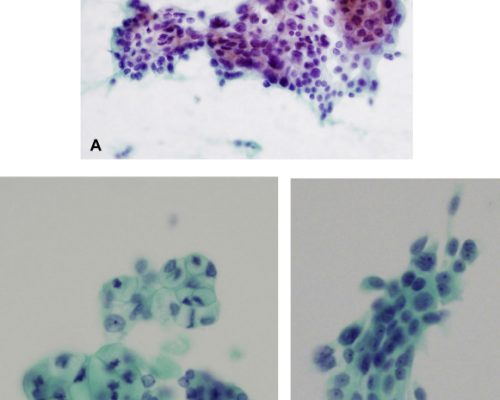
Branches of cytology
There are two main branches of cytology: Exfoliative cytology and Intervention cytology.
1) Exfoliative cytology:
It refers to the examination of cells that are either naturally shed by the patient’s body or manually scraped or brushed from the surface of their tissue. Following are some examples of samples collected through this exfoliative cytology include:
- Gynecological samples: A Pap smear is the most well-known type of this branch. In this type, sample is collected by brushing off cells from your cervix using a swab.
- Gastrointestinal tract samples: These samples are collected during an endoscopy procedure by brushing off cells from the lining of your gastrointestinal tract (your stomach and intestines).
- Skin or mucus samples: These samples are collected by scraping off cells from your skin or mucous membranes, such as the inside of your nose or mouth.
The following samples are some examples of exfoliative cytology which directly collected tissues or fluids that your body naturally sheds.
- Respiratory samples: In this type of sample, the healthcare provider can collect the sample from spit and mucus that you cough up.
- Urinary samples: They are collected from urine.
- Discharge or secretion samples: If you encounter unusual bodily discharge, such as from your eye, vagina, or nipple, your healthcare professional might gather a sample of the discharge for a cytology examination.
2) Intervention Cytology:
Intervention cytology is another branch of cytology which is a medical procedure in which a healthcare professional must intervene in a patient’s body to collect a sample of cells for testing. The commonly employed technique for this procedure is fine-needle aspiration (FNA), where a physician inserts a thin needle into a specific area to extract fluid. Some areas of your body that a pathologist or healthcare provider may perform a fine-needle aspiration include:
- Cysts (fluid-filled lumps) under the skin
- Nodules or masses (solid lumps) under the skin
- Lymph nodes
- Pericardial fluid (fluid in the sac around the heart)
- Pleural fluid (fluid in the space between the lung and the inside of the chest wall)
- Radiologically suspicious areas or nodules of deeper structures (lung, pancreas, thyroid, almost any organ)
Benefits of Cytology testing:
Cytology tests are less invasive and offer several advantages over excisional tissue biopsy. They require only a small sample of cells or fluids, making them less painful and reducing the need for anesthesia. They also have a lower risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding. Additionally, cytology tests allow for easier and quicker sample collection, often in an outpatient setting. Overall, these tests provide valuable information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
When cytology testing is used?
Healthcare providers and pathologists use cytology to diagnose or screen for cancer. When someone shows signs of a potential disease, a diagnostic test like cytology is used to identify abnormal cells. This test effectively categorizes the disease. Healthcare providers also use screening tests, like the Pap smear, to detect diseases like cancer before symptoms appear.
To achieve the desire results in Cytology for any cytologist or cytopathologist requires authentic Reagents, Solvents, Stains etc. One should choose wisely quality products from reputed brands like “TriStains”, which give you reproducible results. TriStains brand meet the highest quality standards & give excellent color performance of desired components of cells and tissue in life science laboratories. “TriStains”, Biological Stains that offer range of stains used in Histology, Cytology, microbiology & Hematology laboratories. Tristains brand was founded with the vision of providing researchers and medical professionals with the best products available in the market. Buy premium quality Biological stain & Indicators from TriStains®. www.tristains.com. All TriStains® Products are exclusively distributed by Dawn Scientific Inc. www.dawnscientific.com.