Buy Gallocyanine (1562-85-2) MF: C15H13N2O5•Cl | MW: 336.73. Get High Quality Gallocyanine (1562-85-2) from Tristains.
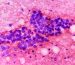
Gallocyanine, also known as 7-Dimethylamino-4-hydroxy-3-oxo-phenoxazine-1-carboxylic acid, is a synthetic dye classified under the oxazine class of dyes. Its chemical formula is C15H13ClN2O5. This dye is recognized for its deep blue to violet color and is commonly utilized in conjunction with chromium (gallocyanine-chrome alum) to improve its staining capabilities. The synthesis of gallocyanine involves the use of a methanol solution of gallic acid in the presence of excess iodine. It is predominantly employed in histological and cytological procedures to stain nucleic acids, creating a distinct contrast with the surrounding tissue.
“TriStains”, Histological Stains/Biological Stains that offer range of stains used in Histology, Cytology, Microbiology and Hematology laboratories. TriStains meet the highest quality standards and give excellent color performance of desired components of cells and tissue in life science laboratories. TriStains series products are carefully tested to ensure accurate, reliable, and reproducible results. Our products are available in different packaging sizes to allow you to get all types of stains & Indicators for your specific purposes from a single source.
In-addition Tristains also deals in numerous Laboratory Supplies, Chemicals, Equipment, Instruments, Reagents, Standard Solutions, Buffers, Histological Stains/Biological Stains & Indicators and many more, for more information please visit our website www.tristains.com or email to sales@tristains.com we will be happy to help you. All Tristains Products are exclusively distributed by Dawn Scientific Inc (https://dawnscientific.com)
Application :
- Gallocyanine is used to stain Nissl bodies (granules of rough endoplasmic reticulum) in neurons, helping to visualize neuronal structures in brain and spinal cord tissues.
- Gallocyanine is used to stain animal cells,mostly the nucleic acids, making it useful for highlighting cell nuclei and chromosomes in tissue sections.
- It is used to stain cell nuclei in cytological preparations, aiding in the examination of cell morphology and pathology, also applied in various cytogenetic techniques to stain chromosomes for karyotyping and genetic studies.
- It is employed in the examination of tissue samples to identify and study abnormalities in cell and tissue structure.
- It is utilized in staining neuronal tissues to study the structure and organization of neurons and neural pathways.
- It also acts as a chelating agent and is used to determine bioactive compounds and several metal ions.
Benefits :
- Selective and precise staining of cell nuclei and chromosomes
- Produces high-contrast stains
- Versatile and stable














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.